Realm Database Tutorial for Android - Part One
October 06, 2017
In this tutorial, we will create a database using Realm Mobile Database and we will perform CRUD operations on the database.
Git Hub Project
The complete project can be cloned from here
Prerequisites
- Please make sure Java and Android Studio IDE are installed on your system.
Reference
Create An Android Application
We will create a new Android application. So from Android Studio, choose File -> New -> New Project. Fill in with your prefer Application name and so on. Then choose Empty Application when you are asked for Add an Activity to Mobile. Finally, we just use the default name for MainActivity at Configure Activity Dialog. Then click Finish.
Add Dependencies
You can check out thhe lastest release from here.
Add this following line to build.gradle(Module:app) and click Sync Now at the top right corner.
classpath "io.realm:realm-gradle-plugin:3.7.2"
Add this following line to build.gradle(Module:app) and click Sync Now at the top right corner.
apply plugin: 'realm-android'
Overall Package and Class layout
This is the overall layout for our project. Person class is Model for our database and PersonRepository will do all the transition between our code and Realm Mobile Database.
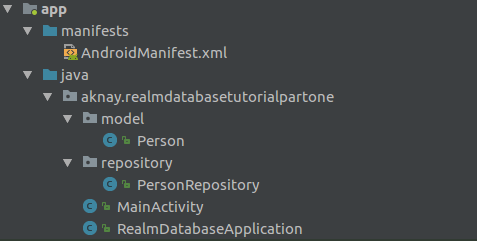
Realm Database Application
First, we need to initialize Realm Database once using Realm.init(this); . We can do it in this RealmDatabaseApplication Class.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import android.app.Application;
import io.realm.Realm;
public class RealmDatabaseApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Realm.init(this);
}
}
Since we create our customized application, we need to register this class to AndroidManifest.xml. Add this line between application tag.
android:name=".RealmDatabaseApplication"
Once you added the above line, the final AndroidManifest.xml will look like this.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="aknay.realmdatabasetutorialpartone">
<application
android:name=".RealmDatabaseApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Crate Person Class
- create package called
model - create class called
PersonPlease, look at the overall layout if you are not sure where to create them.
In order to Realm Database to handle the model, we need Person model class to extend RealmObject. Here we also use @PrimaryKey annotation is to indicate that the id is unique for a person instance.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
import io.realm.RealmObject;
import io.realm.annotations.PrimaryKey;
public class Person extends RealmObject {
@PrimaryKey private long id;
private String name;
private int age;
public void setId(long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
Crate PersonRepository Class
- create package called
repository - create class called
PersonRepository
Again, please look at the overall layout if you are not sure where to create them.
This class handles all CRUD operations for the database. The class use Singleton pattern to get PersonRepository instance so that we will only instantiate only one time. Please note that calling executeTransaction function of mRealm also handle error itself.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import aknay.realmdatabasetutorialpartone.model.Person;
import io.realm.Realm;
import io.realm.RealmResults;
public class PersonRepository {
private PersonRepository() {
mRealm = Realm.getDefaultInstance();
}
private static PersonRepository mPersonRepository = null;
private Realm mRealm = null;
//singleton pattern
public static PersonRepository getInstance() {
if (mPersonRepository == null) {
mPersonRepository = new PersonRepository();
}
return mPersonRepository;
}
public void deleteAll() {
mRealm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(@NonNull Realm realm) {
realm.delete(Person.class);
}
});
}
public void insert(final Person person) {
mRealm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(@NonNull Realm realm) {
realm.copyToRealm(person);
}
});
}
public RealmResults<Person> getAll() {
return mRealm.where(Person.class).findAll();
}
public Person findByName(String name) {
return mRealm.where(Person.class).equalTo("name", name).findFirst();
}
public void update(final Person person) {
mRealm.executeTransaction(new Realm.Transaction() {
@Override
public void execute(@NonNull Realm realm) {
Person personCopy = findByName(person.getName());
personCopy.setAge(person.getAge());
}
});
}
}
MainActivity
Now, this is the fun part. We first create two persons called ‘Joe’ and ‘Bob’. Then we inserted to our database. Please take note that id has to be unique for each person as we set up the id as our PrimaryKey previously. After we added both of them, we list all people in our database. Then, we retrieve back the person by Name. Later we just change Joe age and observe the change.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.util.Log;
import aknay.realmdatabasetutorialpartone.model.Person;
import aknay.realmdatabasetutorialpartone.repository.PersonRepository;
import io.realm.RealmResults;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private String TAG = this.getClass().getSimpleName();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
PersonRepository personRepository = PersonRepository.getInstance();
//new person called 'Joe'
Person joe = new Person();
joe.setId(1); //unique ID
joe.setAge(18);
joe.setName("Joe");
personRepository.insert(joe); //insert to repository
//new person called 'Bob'
Person bob = new Person();
bob.setId(2);
bob.setAge(21);
bob.setName("Bob");
personRepository.insert(bob);
//list all people
RealmResults<Person> results = personRepository.getAll();
for (Person p : results) {
Log.d(TAG, "Person List -> " + "name: " + p.getName() + ", " + "Age: " + p.getAge());
}
//retrieve 'Joe'
Person retrievedJoe = personRepository.findByName("Joe");
Log.d(TAG, "Young Joe -> " + "name: " + retrievedJoe.getName() + ", " + "Age: " + retrievedJoe.getAge());
//update 'Joe' age
joe.setAge(60);
personRepository.update(joe);
//observe the change
Person oldJoe = personRepository.findByName("Joe");
Log.d(TAG, "Old Joe -> " + "name: " + oldJoe.getName() + ", " + "Age: " + oldJoe.getAge());
//delete all entries
personRepository.deleteAll();
}
}
Result
You should see this in log screen.
Person List -> name: Joe, Age: 18
Person List -> name: Bob, Age: 21
Young Joe -> name: Joe, Age: 18
Old Joe -> name: Joe, Age: 60